Troubleshoot
Solutions to common problems when running the FairCom Server
This section identifies possible problems and solutions when running the FairCom server.
troubleshooting guide for FairCom server configuration
troubleshoot configuration
windows
linux
fix configuration
Section | Description |
|---|---|
This section identifies possible problems that may be encountered when using FairCom DB as a Windows service, and ways to diagnose and solve them. | |
This section shows possible options for fixing any issues with connecting to the FairCom DB service. | |
This section shows what an error might look like if you encounter problems starting the FairCom DB service and possible solutions. | |
This sections lists options for solving problems with stopping the FairCom DB service. |
Windows service troubleshooting tips
This section identifies possible problems that may be encountered when using FairCom DB as a Windows service, and ways to diagnose and solve them.
Problems connecting to the FairCom DB service
If client applications are unable to connect to the FairCom DB service, verify that FairCom DB service is running.
CTSTATUS.FCS, typically located in the directory in which the FairCom DB executable resides) for the following information:Are there any error messages logged to
CTSTATUS.FCS?Is the Server Name displayed in
CTSTATUS.FCSthe same server name your client applications are using?Are the protocols displayed in
CTSTATUS.FCSthe same as those your client applications are using?
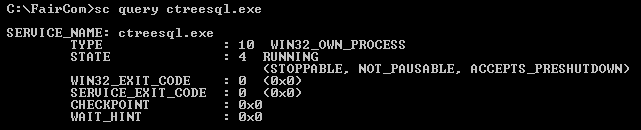
Using sc.exe, run the following (where
"ctreeace.exe"is the name of the FairCom DB service).sc query ctreeace.exe
Using the Windows Services Control Panel applet, open the Control Panel and select the Services applet.
If the FairCom DB service is running, the Status field shows Started.
Otherwise the Status field is blank.
Problems starting the FairCom DB service
If the FairCom DB service fails to start, it returns a service-specific error, and logs a message to the Windows application event log. This information can be used to determine the reason the FairCom server service failed to start. Below is the output of a failed startup when starting the FairCom DB service using FairCom’s SCP. The service-specific error is displayed as the Service Exit code.
Starting the c-tree Server service... c-treeServer start unsuccessful: Current State: STOPPED Win32 Exit: 1066 Service Exit: 6 Checkpoint: 0x0 WaitHint: 0x0
The Table 1, “FairCom's service errors” shows possible service-specific errors returned by the FairCom server service, the corresponding message, and possible causes for each of these errors.
Error code | Error message | Possible causes |
|---|---|---|
2 | (Varies) | An operating system function call failed. See the event log for a detailed error message. |
4 | The FairCom DB settings file is missing. It is required to operate this server. | FairCom DB service requires a settings file, but it was not found. |
5 | The current settings file are invalid. | FairCom DB requires a settings file, and the settings file that was found was not valid. Contact your application developer for assistance. |
6 | FairCom DB must be activated with a FairCom activation key to operate, see the FairCom DB activation key card within your package for more information. | FairCom DB has not yet been activated. |
Start the Event Viewer.
Select the Application log option from the Log menu.
Events logged by the FairCom DB service have the Source field set to the service name (
“c-treeACE Database Engine"or"c-treeEDGE Database Engine"by default).Double-click an event to display the event detail.
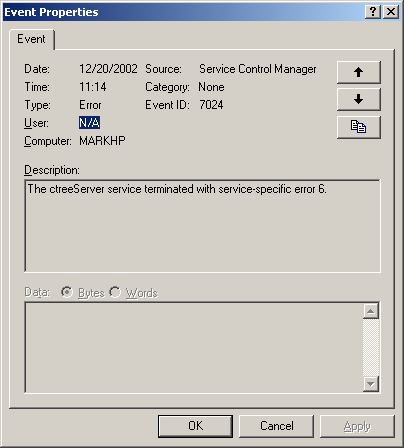
Event Viewer displays events that are logged by the FairCom DB service
Problems stopping the FairCom DB service
Check the event log for an error message.
Check for error messages in the FairCom DB status log file (
CTSTATUS.FCS, typically located in the directory in which FairCom DB executable resides).FairCom’s ctadmn utility (provided with the FairCom server) can also be used to stop the FairCom DB service.
FairCom server not running
If your server quits immediately after you try to launch it, you may already have a server running in the background with the same port settings. Or you may have another application already using ports required by the FairCom server, see Configure ports for v12.x.
Important
The evaluation version of the product times out after three hours and shuts down the server. Therefore, the server needs to be restarted every three hours.
Problem: Web browser cannot connect to locally running FairCom Server
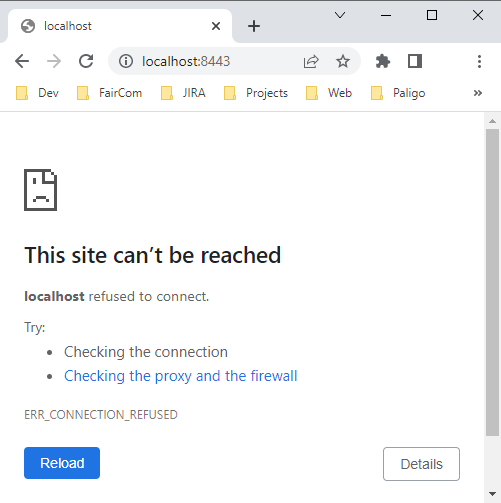
The error that is received when there are issues connecting to FairCom's browser-based applications
Solution: Use 127.0.0.1 instead of localhost
127.0.0.1 instead of localhost:To test FairCom database web tools use use http://127.0.0.1:8080/ or https://127.0.0.1:8443/ instead of http://localhost:8080/ or https://localhost:8443/.
It is best practice to use
127.0.0.1instead oflocalhostto ensure you connect to your local computer becauselocalhostdoes not work reliably in some languages, such as Python. Also, your computer'shostsfiles and/or DNS settings may be configured to redirect thelocalhostdomain name to another computer besides your local computer.If you use
127.0.0.1you do not have to worry about the behavior oflocalhostand thehostsfile.If you want to verify how your
hostsfile modifies the behavior oflocalhost, you can open it in any editor to see what IP address it maps tolocalhost.In Windows, the
hostsfile is located inC:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc.By default, it uses DNS to map
localhost. Your DNS server typically mapslocalhostto127.0.0.1, but it can map it anywhere and this can cause problems.In Linux (Unix), the
hostsfile is located in the/etcfolder.By default, Linus maps
localhostto127.0.0.1.
Note
Use the Google Chrome browser for FairCom browser-based tools. Other browsers may cause unexpected behavior.
Some FairCom Scripts require Python 3.
If a FairCom script requires Python 3, you might need to install it. This document shows how to install Python 3 on Windows.
Python 3 comes preinstalled on most MacOS and Linux distributions.
Use the command line to determine if Python is already installed. Open a command prompt (Start+R cmd).
py --version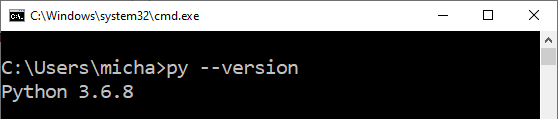
If the current version of Python is at least Python 3.7.9, you do not need to install Python.
Uninstall previously installed versions of Python. This ensures you can run only the newly installed version of Python.
Open the Apps & Features dialog to add or remove programs.
Search for Python.
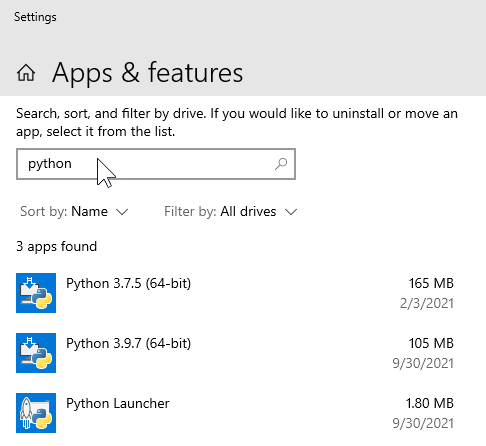
Uninstall existing versions
Verify no instances of Python are installed by running the following command and ensuring it returns no files:
where.exe python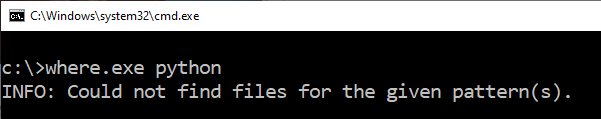
Remove all Python programs from the path.
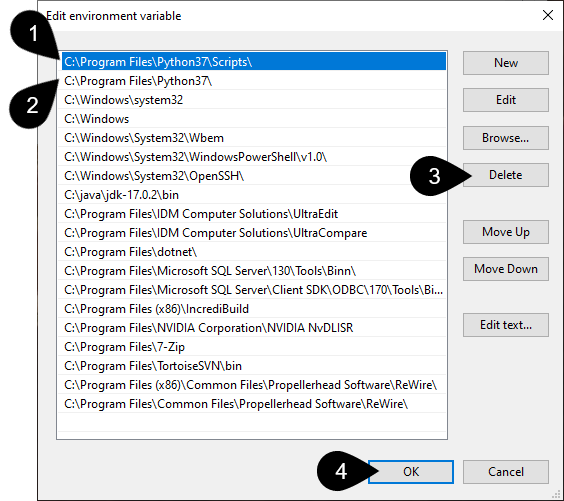
Open System Properties -> Environment Variables -> System Variables -> Path
Click each path containing a reference to Python and click the delete button.
Click OK.
Download a Windows x86-64 executable installer for Python, such as Python 3.12.3
Download the Windows installer (64-bit) for an Intel-based PC or the Windows installer (ARM64) for the less common ARM-based PC.
This downloads an executable with a name like python-3.12.3-amd64.exe
Run the downloaded executable.
Click Add python.exe to PATH
Click Customize installation
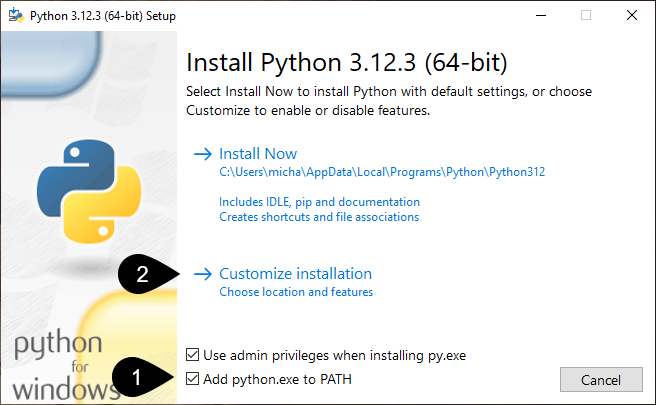
Click Next
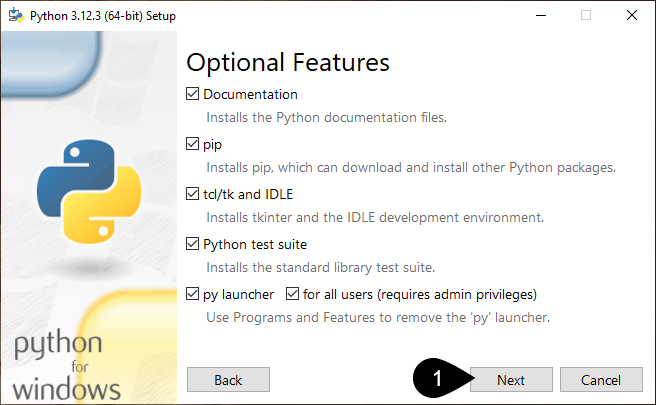
Configure install options.
Check the box: Install for all users
Ensure Add Python to environment variables is checked.
Click Install
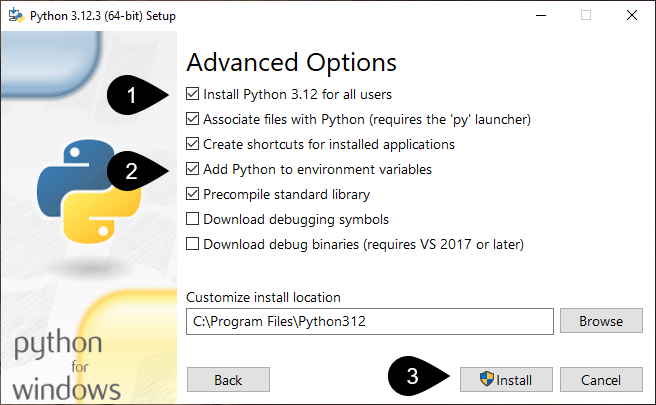
Wait for the following screen to appear.
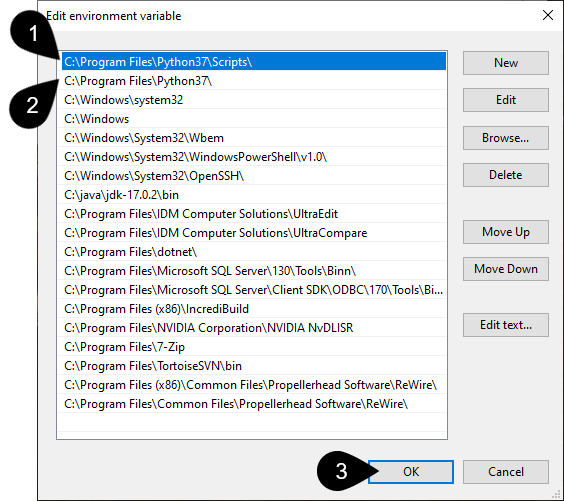
Verify the path environment variables are correct.
There should be two paths for the specific version of Python you installed: one for Python itself and another for Python scripts.
Click OK.
Using the command line, verify the version of Python matches the version you installed.
py --versionwhere.exe python
Installation guide for Python 3 on Windows
The FairCom server adds a log entry to ctstatus.fcs whenever it disconnects a MQTT client, terminates a JSON API session, refuses a connection attempt, or fails to process certain requests because of a limit violation.
To prevent the log from overflowing with log entries, the server implements an internal in-memory counter for each subsequent limit violation of the same type. For every 10 violations up to 100 violations, the server writes another log entry. For every 100 violations up to 1000 violations, the server writes another log entry. For every 1000 violations from then on, the server writes another log entry. For every 10,000 violations, reset the counter to zero to ensure the server adds another round of log messages to the log file. This functionality keeps the issue visible in the log without overflowing it.
Limits set by your license file or by the following properties can cause these to happen:
Property | Notes |
|---|---|
(config/services.json file) | This property limits the number of simultaneous TCP/IP connections each IP Address/host computer can make to the FairCom server on a "per listener" and/or "global" basis. When exceeded, the server will not accept additional TCP/IP connections from that host. This affects HTTP, HTTPS, MQTT, MQTTS, WS, and WSS connections. |
jsonActionApiDefaults.maxJsonApiSessions (config/services.json file) | This property limits the number of simultaneous JSON API sessions the FairCom server will allow at any given time, up to the number allowed by your license. When exceeded, |
jsonActionApiDefaults.maxJsonApiSessionsPerIpAddress (config/services.json file) | This property limits the number of simultaneous JSON API sessions the FairCom server will allow per IP Address/host computer. When exceeded, |
jsonActionApiDefaults.maxJsonApiSessionsPerUsername (config/services.json file) | This property limits the number of simultaneous JSON API sessions the FairCom server will allow per username. Usernames are created by setting the |
(configureTopic action) | This property specifies how long the MQTT broker is willing to wait for the next packet from the client during a QoS 1 or 2 PUBLISH handshake. If this limit is exceeded, the broker will disconnect the client. Slow or overloaded servers might benefit from increasing this number. If that does not help, reduce MQTT message traffic or use a more powerful server. |
(createSession & alterSession actions) | This property specifies how long a JSON API session (created with the |