Modbus Tutorials
Modbus tutorials for FairCom Edge
Ensure the FairCom server is installed and running.
Confirm server access by running the FairCom API Explorer. The typical URL is
https://localhost:8443/.
This page will contain tutorials on how to connect FairCom Edge to Modbus
This quickstart tutorial walks through how to capture, store, transform, forward, and query data using the Modbus simulator.
Launch the open-source Modbus simulator that is included with the package to change the simulated data.
Open a command prompt.
Navigate to the simulator in
<FairCom Folder>/server/modbus/test/<OS folder>/diagslave.<#.##>/<OS version folder>/.Run the following command at the command prompt to start the Modbus simulator that will answer Modbus requests.
diagslave -m tcp -p 502
Connect to the
"diagslave"and set the defined Modbus data item.Open another command prompt.
Navigate to
<FairCom Folder>/server/modbus/test/<OS folder>/modpoll-<#.##>/<OS version folder>/.Run modpoll to create data.
Note
You can run it multiple times with different parameters to change the Modbus data.
modpoll -m tcp -p 502 -a 5 -r 1200 -c 1 localhost 65
modpoll -m tcp -p 502 -a 5 -r 1200 -t 0 -c 1 localhost 1
modpoll -m tcp -p 502 -a 5 -r 1300 -c 2 localhost 0x47F1 0x2000
Note
The Modbus simulator will answer the Modbus TCP requests with the following data items:
"temperature"Temperature is a register containing an integer number.
"volume"Volume is a register containing a floating point number.
"status"Status is a coil containing a Boolean.
Start the FairCom browser-based tools.
The tools icons appear.
Select and log into Data Explorer.
The Data Explorer interface window appears.
Click the API Explorer tab.
The API Explorer interface opens and the Server navigation window shows that you are connected to the FairCom database and the FairCom server. Use the FairCom database or another database you create to store the "customer tables".
This procedure creates an input named "modbusTCP" that takes Modbus TCP data and stores it in JSON format in the payload field of records in a table named "modbusTableTCP" in the "faircom" database.
Select Hub API from the Select API dropdown menu.
Select
createInputfrom the JSON Actions dropdown menu.Replace the JSON in the API Request editor with the following JSON:
{ "api": "hub", "action": "createInput", "params": { "inputName": "modbusTCP", "serviceName": "modbus", "settings": { "modbusProtocol": "TCP", "modbusServer": "127.0.0.1", "modbusServerPort": 502, "modbusDataCollectionIntervalMilliseconds": 15000, "propertyMapList": [ { "propertyPath": "temperature", "modbusDataAddress": 1199, "modbusDataAccess": "inputRegister", "modbusUnitId": 5, "modbusDataLen": 1 }, { "propertyPath": "volume", "modbusDataAddress": 1299, "modbusDataAccess": "inputRegister", "modbusUnitId": 5, "modbusDataLen": 2 }, { "propertyPath": "status", "modbusDataAddress": 1199, "modbusDataAccess": "coil", "modbusUnitId": 5, "modbusDataLen": 1 } ] }, "schemaName": "admin", "tableName": "modbusTableTCP", "databaseName": "faircom", "retentionPolicy": "autoPurge", "retentionPeriod": 30, "retentionUnit": "day", "metadata": { } }, "authToken": "replaceWithAuthTokenFromCreateSession" }Click Apply defaults to JSON request (
) to replace the
"authToken"value with the valid one from your session.Click Send request (
 ) to issue the JSON-based request.
) to issue the JSON-based request.Observe the response and ensure the action is completed successfully.
Note
"errorCode"with a value of0indicates success."errorCode"with a non-zero value indicates a failure. See Errors and contact FairCom for more information about an error.
Start the FairCom Data Explorer.
Navigate to and select modbustabletcp in the Server navigation window through
faircom>admin>Tables.Click the Table Records tab (
 ).
).Note
The table records are displayed as one record per row.
Select a record and click the
source_payloadfield.Observe the JSON contents of the field. Click the "edit" icon of the
source_payloadfield to see the content formatted as JSON.
Note
If the table has no records, look at <faircom>/data/CTSTATUS.FCS to see errors related to the connector.
This procedure creates a transform named "transform_modbus1" that will transform the JSON-based data from the "modbusTableTCP" table into fields in a new table called "modbus1" in the FairCom database.
Select from the Select API dropdown menu.
Select
"createTransform"from the JSON Actions dropdown menu.Replace the JSON in the API Request editor with the following JSON:
{ "api":"hub", "action":"createTransform", "params": { "transformName":"transform_modbus1", "transformActions":[ { "inputFields":["source_payload"], "transformStepMethod":"jsonToDifferentTableFields", "outputFields":[ "temperature", "volume", "status" ], "transformParams": { "targetTableName":"modbus1", "mapOfPropertiesToFields":[ { "propertyPath":"temperature", "name":"temperature", "type":"integer" }, { "propertyPath":"volume", "name":"volume", "type":"float" }, { "propertyPath": "status", "name": "status", "type": "bit" } ] } } ] }, "authToken": "replaceWithAuthTokenFromCreateSession" }Click Send request (
 ).
).Observe the response and ensure the action is completed successfully.
Note
"errorCode"with a value of0indicates success."errorCode"with a non-zero value indicates a failure. See Errors and contact FairCom for more information about an error.
Once the transform has been created, alter the input so that data added to the "modbusTableTCP" table will also be stored in rows in the "modbus1" table.
Select Hub API from the Select API dropdown menu.
Select
alterInputfrom the JSON Actions dropdown menu.Replace the JSON in the API Request editor with the following JSON:
{ "api": "hub", "action": "alterInput", "params": { "inputName": "modbusTCP", "transformName": "transform_modbus1" }, "authToken": "replaceWithAuthTokenFromCreateSession" }Click Send request (
 ).
).Observe the response and ensure the action is completed successfully.
Note
"errorCode"with a value of0indicates success."errorCode"with a non-zero value indicates a failure. See Errors and contact FairCom for more information about an error.
View the "modbus1" table in the "faircom" database for the transformed data.
Both of the following procedures will let you view the transformed data. You can use either of these procedures to view the transformed data.
View transformed data through the Server navigation window
Select the faircom database in the Server navigation window.
Select Connect from the JSON Actions dropdown menu.
Navigate to and select the modbus1 table in the Server navigation window through
faircom>admin>Tables>.Click the Table Records tab (
 ).
).Note
The table records are displayed as one record per row.
Observe the table records.
View transformed data through a SQL query
Click the SQL Queries tab (
 ).
).Enter the following SQL query in the textbox.
select * from modbus1 where temperature > 60;
Click the Execute SQL statement button (
 ).
).Observe the response and ensure the action is completed successfully.
Once Modbus TCP data is flowing into a table as JSON and is being transformed into discrete fields in another table, Forward the data out over MQTT.
Select MQ API from the Select API dropdown menu.
Select
configureTopicfrom the JSON Actions dropdown menu.Replace the JSON in the API Request editor with the following JSON:
{ "api": "mq", "action": "configureTopic", "params": { "topic": "modbusForward", "databaseName": "faircom", "tableName": "modbusTableTCP" }, "authToken": "replaceWithAuthTokenFromCreateSession" }Click Send request (
 ).
).Observe the response and ensure the action is completed successfully.
Note
"errorCode"with a value of0indicates success."errorCode"with a non-zero value indicates a failure. See Errors and contact FairCom for more information about an error.
Start the FairCom Browser-Based tools.
Select and connect to MQ Explorer.
Select MQTT Management from the Control menu (
 ).
).Click (
 ) to open the Manage Subscriptions window.
) to open the Manage Subscriptions window.Select the topic you subscribed to from the Topic dropdown menu.
Click (
 ).
).Close the Manage Subscriptions window.
Observe your message, displayed under Incoming Messages every 10 seconds.
Click (
 ).
).Delete your subscription from the list.
Select DB API from the Select API dropdown menu.
Select the
getRecordsByIndexfrom the JSON Actions dropdown menu.Replace the JSON in the API Request editor with the following JSON:
{ "api": "db", "action": "getRecordsByIndex", "params": { "databaseName": "faircom", "tableName": "modbus1", "indexName": "ts_index" }, "authToken": "replaceWithAuthTokenFromCreateSession" }Click Send request (
 ).
).Observe the API Response response and ensure the action is completed successfully.
Note
"errorCode"with a value of0indicates success."errorCode"with a non-zero value indicates a failure. See Errors and contact FairCom for more information about an error.
The following example configures a Modbus connector to output data to a Modbus device. When MQTT, SQL, JSON DB, or an input connector inserts a record into the "modbus1" integration table, the FairCom server delivers the record to the Modbus connector. This example configures the Modbus connector to extract the value of the temperature property from the record’s source_payload field and write it to a device using the Modbus protocol.
Select Hub API from the Select API dropdown menu.
Select
createOutputfrom the JSON Actions dropdown menu.Replace the JSON in the API Request editor with the following JSON:
{ "api": "hub", "action": "createOutput", "params": { "outputName": "writeTemperatureToModbus", "serviceName": "modbus", "databaseName": "faircom", "ownerName": "admin", "tableName": "modbusTableTCP", "sourceFields": ["source_payload"], "settings": { "modbusProtocol": "TCP", "modbusServer": "127.0.0.1", "modbusServerPort": 502, "propertyMapList": [ { "propertyPath": "source_payload.temperature", "modbusDataAddress": 1399, "modbusDataAccess": "holdingregister", "modbusUnitId": 5, "modbusDataLen": 1 } ] } }, "authToken": "replaceWithAuthTokenFromCreateSession" }Click Apply defaults to JSON request (
) to replace the
"authToken"value with the valid one from your session.Click Send request (
 ) to issue the JSON-based request.
) to issue the JSON-based request.Observe the response and ensure the action is completed successfully.
Note
"errorCode"with a value of0indicates success."errorCode"with a non-zero value indicates a failure. See Errors and contact FairCom for more information about an error.
This procedure creates an Input with OPC to collect data that will then be used to write to Modbus. So, FairCom Edge will work as a converter between those protocols. This tutorial is geared toward the windows operating system. However, similar operations will work on Linux and other platforms.
Launch the OPC UA server simulator
Open a command prompt and find the server in
<faircom>/server/opc/test/open62541_v0.30/<OS version folder>/.Run the program called
server_cttto emulate an OPC UA device and answer OPC UA requests.Leave the OPC UA server running.
Capture OPC UA data as JSON records in the database
This procedure creates an input named
opcDS2. TheopcDS2input takes OPC UA data and stores it in the JSON format in the payload field of records in a table. The table is namedopctable2in the FairCom database.Start the FairCom Data Explorer and go to API Explorer.
Replace the JSON in the API Request editor with the following JSON:
{ "api": "hub", "action": "createInput", "params": { "inputName": "opcDS2", "serviceName": "opcua", "settings": { "opcServerUrl": "opc.tcp://localhost:4840", "opcDataCollectionIntervalMilliseconds": 5000, "propertyMapList": [ { "propertyPath": "the_answer", "opcNamespace": 1, "opcNodeName": "the.answer" } ] }, "ownerName": "admin", "tableName": "opcTable2", "databaseName": "faircom", "retentionPolicy": "autoPurge", "retentionPeriod": 30, "retentionUnit": "day", "metadata": { } }, "authToken": "replaceWithAuthTokenFromCreateSession" }Click Apply defaults to JSON request (
 ) to replace the
) to replace the "authToken"with a valid token from your session.Click Send request (
 ) to issue the JSON-based command.
) to issue the JSON-based command.Observe the response and ensure the action is completed successfully.
Note
An
"errorCode"with a value of0indicates success. An"errorCode"with a non-zero value indicates a failure. See Errors and contact FairCom for more information about an error.
View the captured OPC UA data in the
opcTable2tableNavigate to and select opctable2 in the Server navigation window through
faircom>admin>Tables>opctable2.Click the Table Records tab (
 ).
).Click the
"source_payload"field for the record you wish to view.Observe the JSON contents of the field in the Edit Record window by clicking on the
"source_payload"field.{ "create_ts":"2025-03-27T21:11:52.117Z", "the_answer":42 }
Start the Modbus Server simulator
Open a new command prompt.
Navigate to the simulator in
<FairCom Folder>/server/modbus/test/<OS folder>/diagslave.<#.##>/<OS version folder>/.Run diagslaveTCP.
Leave diagslaveTCP running.
Define an integration to write data to Modbus from the same table (createOutput)
Similar to step 2, execute this API request:
{ "api": "hub", "action": "createOutput", "params": { "outputName": "opc_to_modbus", "serviceName": "modbus", "tableName": "opcTable2", "sourceFields": ["source_payload"], "settings": { "modbusProtocol": "TCP", "modbusServer": "127.0.0.1", "modbusServerPort": 502, "modbusDataAddressType": "oneBased", "propertyMapList": [ { "propertyPath": "source_payload.the_answer", "modbusDataAddress": 1200, "modbusDataAccess": "holdingregister", "modbusSlave": 5, "modbusDataType": "int16SignedAB", "modbusDataLen": 1 } ] } }, "authToken": "replaceWithAuthTokenFromCreateSession" }This command will read
opcTable2and write"the_answer"value to modbus at address 1200.Read data at Modbus address 1200
Open a new command prompt.
Navigate to the simulator in
<FairCom Folder>/server/modbus/test/<OS folder>/modpoll-<#.##>/<OS version folder>/.Run this:
modpoll -m tcp -p 502 -r 1200 -c 3 -1 -a 5 localhost
You will see:
[1200]: 42 [1201]: 0 [1202]: 0
Change OPC data and observe that Modbus will receive a new value
Open a command prompt and find the OPC client in
<faircom>/server/opc/test/open62541_v0.30/<OS version folder>/.Run the program called client to connect to server_ctt and increment the defined OPC UA variables by
2.Read Modbus data again to see the new value (Step 6)
modpoll -m tcp -p 502 -r 1200 -c 3 -1 -a 5 localhost
You will see:
[1200]: 44 [1201]: 0 [1202]: 0
Modbus devices prefer to store integer numbers in their registers, but a machine often needs to deliver floating point numbers to the customer. Modbus devices typically use one of four techniques to represent a floating point number:
Store an integer number in a register and let the customer divide it by a number, such as
7014divided by100to create70.14.Store two integer numbers in two registers, such as
70and14, and let the customer append them to create70.14.Same as #2 but the registers are in reverse order.
Store the bytes of an IEEE Floating point number in multiple registers, and let the customer combine them, such as
0x428C47AErepresenting70.14.
FairCom's Modbus connector supports all four techniques when it collects data from registers and converts it into JSON numbers.
Dividing collected integers
The machine stores an integer number in a register and requires the customer to divide it by a number, such as 10, 100, or 1000, to create a floating-point number.
FairCom's Modbus connector uses the following JSON configuration to convert the integer value
7014in register address2000into70.14.
{ "propertyPath": "temperature", "modbusDataAddress": 2000, "modbusDataAccess": "holdingregister", "modbusUnitId": 5, "modbusDataLen": 1, "modbusRegisterType": "int16SignedAB", "modbusConvertToFloat": "divideByInteger", "modbusDivisor": 100 },To configure the Modbus connector to convert an integer into a floating point number, add the
"modbusConvertToFloat": "divideByInteger"and"modbusDivisor": 100settings to the configuration. You can set"modbusDivisor"to10,100,1000,10000, or another integer number. The connector reads the value of the Modbus register, divides it by the integer number in the"modbusDivisor"property, and stores the result at the"propertyPath"location in the JSON document it generates.
Storing two separate integers
The machine stores two integer numbers in two registers to represent one floating point number.
FairCom's Modbus connector uses the following JSON configuration to convert the integer value
70in the specified register and14in the next register into70.14. FairCom's Modbus connector always considers the decimal number as positive. So, if the value read is -14, for example, it will be converted to 14.
{ "propertyPath": "temperature", "modbusDataAddress": 2000, "modbusDataAccess": "holdingregister", "modbusUnitId": 5, "modbusDataLen": 1, "modbusRegisterType": "int16SignedAB", "modbusDecimalDigits":2, "modbusConvertToFloat": "appendAdjacentRegisters" },To configure the Modbus connector to convert integers in successive registers into a floating point number, add the
"modbusConvertToFloat": "appendAdjacentRegisters "setting to the configuration. The connector reads the value of the specified Modbus register and the next register and appends them with a decimal point between them. It stores the result at the"propertyPath"location in the JSON document it generates.If you are using this configuration with a createOutput command, it is necessary to change
"modbusDecimalDigits"to properly convert the float number to two integers. The default value is2.
Storing two separate integers in reverse order
Store two integer numbers in two registers to represent one floating point number, but the fractional part is in the first register.
FairCom's Modbus connector uses the following JSON configuration to convert the integer value
14in the specified register and70in the next register into70.14.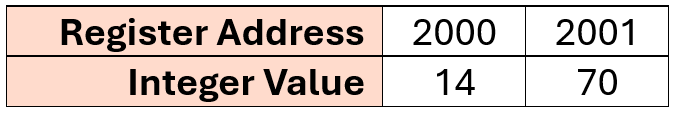
{ "propertyPath": "temperature", "modbusDataAddress": 2000, "modbusDataAccess": "holdingregister", "modbusUnitId": 5, "modbusDataLen": 1, "modbusRegisterType": "int16SignedAB", "modbusDecimalDigits":2, "modbusConvertToFloat": "appendAdjacentRegistersReversed" },To configure the Modbus connector to convert integers in successive registers into a floating point number, add the
"modbusConvertToFloat": "appendAdjacentRegisters"setting to the configuration. The connector reads the value of the specified Modbus register and the next register and appends them with a decimal point between them. It stores the result at the"propertyPath"location in the JSON document it generates.If you are using this configuration with a createOutput command, it is necessary to change
"modbusDecimalDigits"to properly convert the float number to two integers. The default value is2.
Storing the bytes of an IEEE floating point number
Store the bytes of an IEEE Floating point number in multiple registers.
FairCom's Modbus connector uses the following JSON configuration to convert the IEEE bytes stored in two registers. For example, the first two bytes,
0x428C, can be stored in register2000, and the bytes0x47AEcan be stored in register2001. The connector reads the bytes in both registers, combines them into four bytes, and treats them as an IEEE floating point number representing70.14.
{ "propertyPath": "temperature", "modbusDataAddress": 2000, "modbusDataAccess": "holdingregister", "modbusUnitId": 5, "modbusDataLen": 2, "modbusRegisterType": "ieeefloat32ABCD" },To configure the Modbus connector to convert the bytes of an IEEE floating point number in successive registers into a floating point number, add the
"modbusRegisterType": "ieeefloat32ABCD"setting to the configuration. You can assign any of the following values to"modbusRegisterType"to specify different byte orders and sizes of IEEE floating point numbers:"ieeeFloat32ABCD""ieeeFloat32CDAB""ieeeFloat32DCBA""ieeeFloat32BADC""ieeeFloat64ABCDEFGH""ieeeFloat64BADCFEHG""ieeeFloat64CDABGHEF""ieeeFloat64DCBAHGFE""ieeeFloat64HGFEDCBA""ieeeFloat64GHEFCDAB""ieeeFloat64FEHGBADC""ieeeFloat64EFGHABCD"