<faircom>\drivers\sql.jdbc\tutorials\JDBC_Tutorial2.java
Now we will build some table/file relationships using the FairCom DB JDBC Interface.
This tutorial will advance the concepts introduced in the first tutorial by expanding the number of tables. We will define key columns/fields and create specific indexes for each table to form a relational model database.
Like all other examples in the c-tree tutorial series, this tutorial simplifies the creation and use of a database into four simple steps: Initialize(), Define(), Manage(), and You’re Done() !
Tutorial #2: Relational Model and Indexing
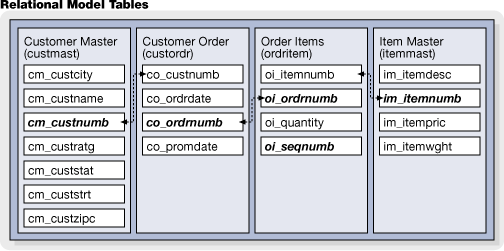
Here we add a bit more complexity, introducing multiple tables, with related indices in order to form a simple "relational" database simulating an Order Entry system. Here is an overview of what will be created:
Note our simple Main() function:
import java.sql.*;
import java.io.*;
public class JDBC_Tutorial2 {
static Connection conn;
static Statement stmt;
//
// main()
//
// The main() function implements the concept of "init, define, manage
// and you're done..."
//
public static void main (String[] args)
throws java.io.IOException
{
Initialize();
Define();
Manage();
Done();
System.out.print("\nPress <ENTER> key to exit . . .");
System.in.read();
System.exit(0);
}
We suggest opening the source code with your own editor.
Continue now to review these four steps.